Create a child dataset
Child datasets allow you to create filtered views of existing datasets without affecting the original data. This is perfect for focusing on specific subsets of your data while maintaining a connection to the parent dataset.
Prerequisites
Before creating a child dataset, you'll need an existing dataset to work with. If you haven't created one yet, check out our dataset creation guides (using EraQL or from existing tables) and return here once your dataset is ready.
Creating Your Child Dataset
Navigate to the dataset you want to create a child dataset from. Look for the three dots menu associated with that dataset and click it to reveal the available options.
From the menu, select Create Child Dataset. This opens the child dataset configuration interface.
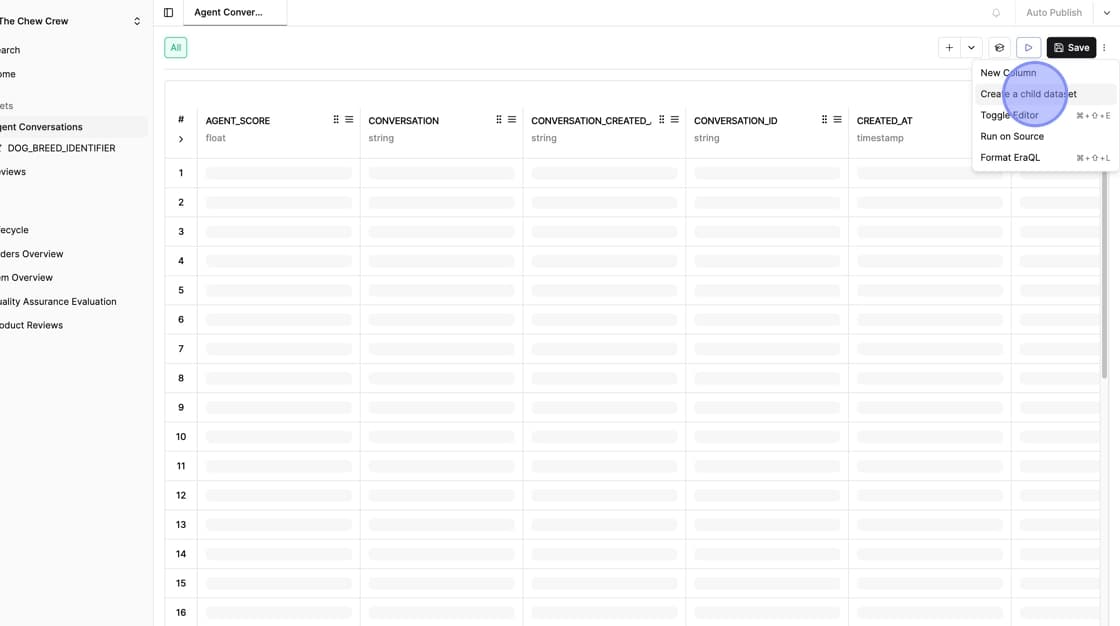
Setting Up Filters
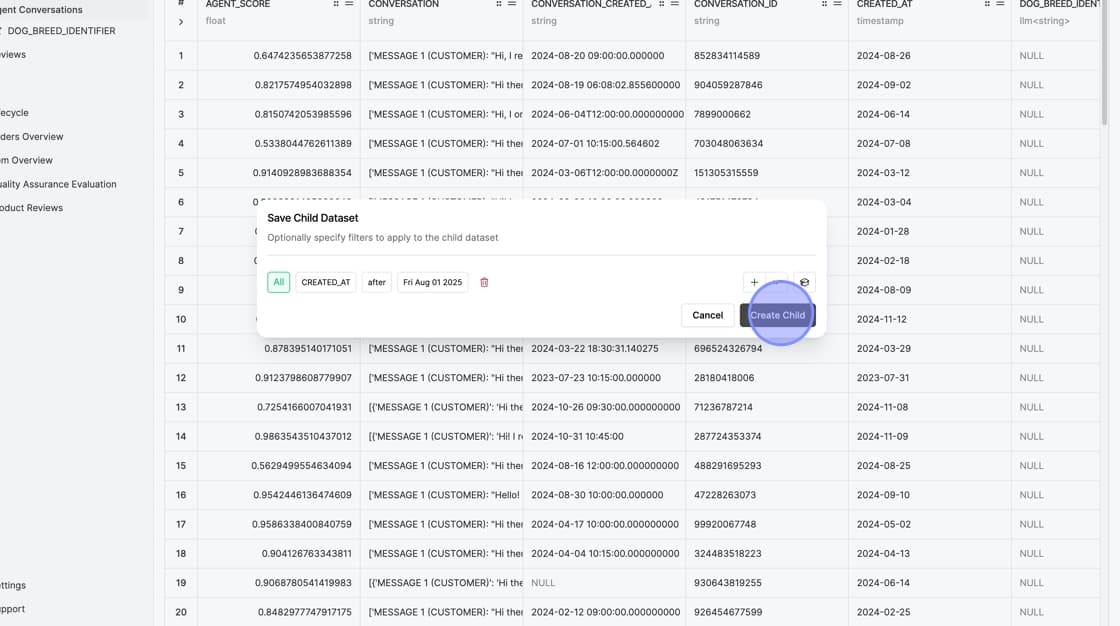
A dialog box will appear where you can configure filters for your child dataset. This is where you specify what subset of data you want to focus on.
Enter your filter criteria using standard comparison operators. For example, to filter for recent entries, you might use:
"review_created_at" > @2025-08-01
This creates a child dataset containing only records created after August 1st, 2025.
Naming and Saving
After setting your filters, you'll be prompted to provide a name for your child dataset. Choose something descriptive that clearly indicates what the filtered data contains.
For our example filtering recent reviews, a name like "August 2025+" clearly communicates the time range covered.
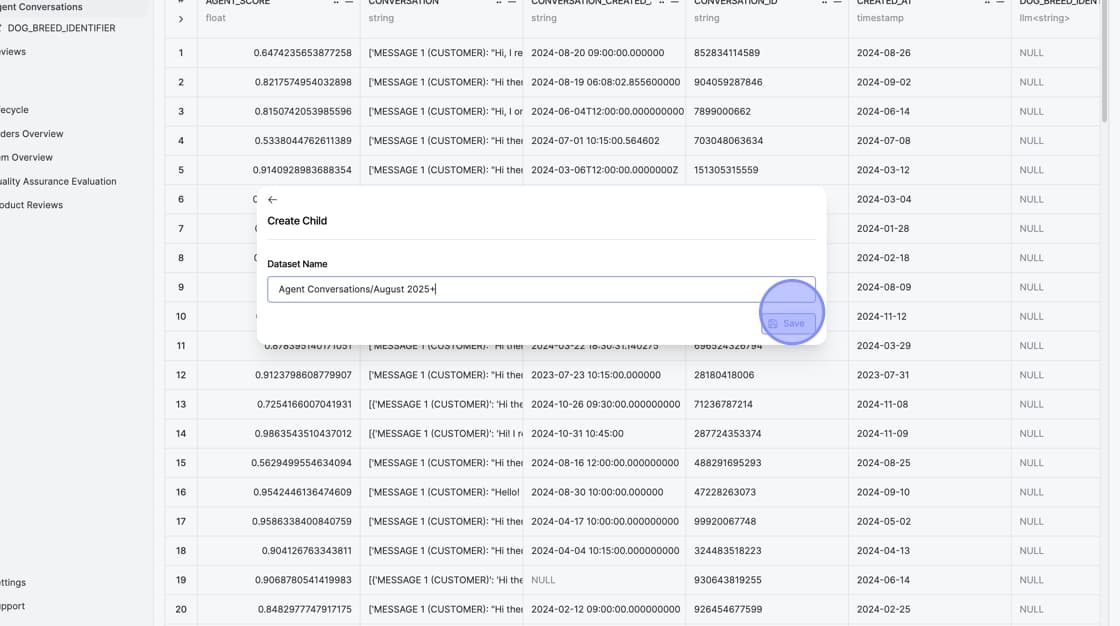
Click Save to create your child dataset.
Accessing Your Child Dataset
Your new child dataset will appear nested under its parent dataset in the left-hand sidebar. You can expand the parent dataset to see all its children and click on any child dataset to open it.
The child dataset maintains its connection to the parent while providing a focused view of your filtered data. Any updates to the parent dataset will automatically flow through to the child, but the child's filters remain intact.
Why Use Child Datasets?
Child datasets are perfect for:
- Creating focused views for specific time periods
- Filtering data for particular categories or segments
- Testing analysis on subsets before applying to full datasets
- Organizing data for different team members or use cases
Your child dataset now provides a targeted view of your data while maintaining the benefits of the parent dataset's structure and any ongoing updates.